How to Resolve the Filename or Extension Is Too Long?
In the digital age, file management is a crucial aspect of both personal and professional computing. Whether you’re organizing documents, backing up files, or sharing data with others, managing files efficiently is essential. However, despite advancements in technology, certain limitations remain—one of which is the “filename or extension is too long” error. This seemingly simple issue can lead to significant headaches for users who encounter it, especially when handling large numbers of files or deeply nested directory structures. This article explores the causes of this error, its implications, and provides practical solutions to help you manage your files more effectively.
1. What Causes the Error?
The “filename or extension is too long” error primarily occurs because of limitations within the operating system, specifically in Windows. The Windows operating system has a path length limit of 260 characters, and this limit includes the drive letter, colon, backslashes, directory names, and the file name itself. When a file path exceeds this limit, Windows may prevent you from accessing, renaming, or moving the file, triggering the error.
For example, if you have a file with a lengthy name located deep within several nested folders, the total path length might exceed 260 characters, leading to the error. This issue can be particularly troublesome for users who work with complex file structures, such as software developers, data analysts, or those managing large archives.
2. How to Resolve the Filename or Extension Is Too Long?
The problem “filename or extension is too long” can be fixed in the following methods:
2.1 Enable Long Path Support in Windows 10/11
Windows 10 (from version 1607) and Windows 11 allow paths longer than 260 characters, but this feature must be enabled manually.
To enable long path support:
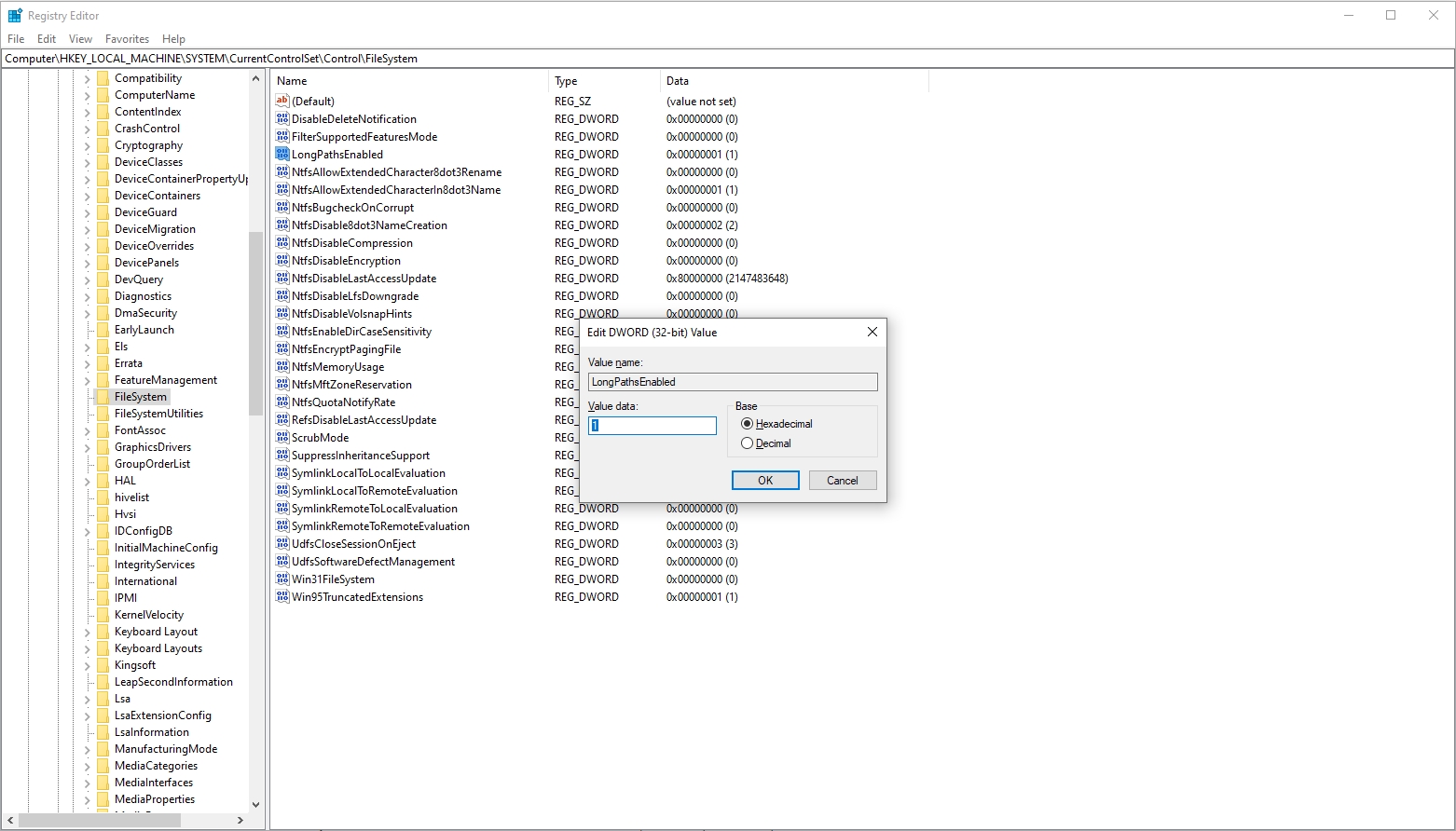
- Open the Registry Editor: Hit “Win + R“, type “regedit“, then hit “Enter“.
- Navigate to the Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem
- Enable Long Paths: Find the LongPathsEnabled entry, double-click it, and set its value to 1.
- Reboot Your Computer: To have the modifications take effect, restart your computer.
2.2 Shorten the File Path
One of the most straightforward solutions is to shorten the file path by moving the file or folder to a higher-level directory. For example, instead of keeping a file in a deeply nested structure like C:\Users\YourUsername\Documents\Projects\ProjectName\Subfolder\AnotherSubfolder\file.txt, move it to a simpler path like C:\Projects\file.txt.
This reduces the total path length and helps avoid the error. Although this method is effective, it may require some reorganization of your files and folders, which could be inconvenient if you have a well-established structure.
2.3 Use Command Prompt or PowerShell
If you encounter difficulties accessing files with long paths using File Explorer, you can use Command Prompt or PowerShell, which often handle longer paths better.
- Using Command Prompt: Open Command Prompt (
cmd) and use thecdcommand to navigate to the directory containing the file. You can then use commands likerenameormoveto rename or move the file. - Using PowerShell: PowerShell scripts can also be used to manipulate files with long paths. For example, you can use a script to automate the renaming or moving of files to a shorter path.
2.4 Map a Network Drive
In environments with deeply nested folder structures, you can map a network drive to a folder closer to the root directory. This effectively shortens the path length for files within that folder.
To map a network drive:
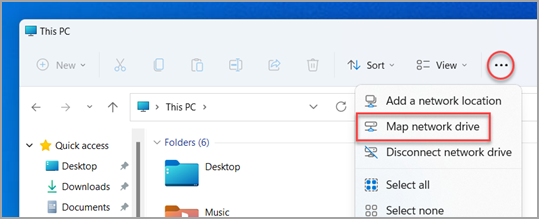
- Activate File Explorer, then right-click on “This PC” and select “Map network drive“.
- Choose a Drive Letter and select the folder you want to map.
- Complete the Mapping Process.
Once mapped, you can access the files as if they were located at the root of the drive, reducing the risk of encountering the “filename or extension is too long” error.
2.5 Use Third-Party Tools
Long file paths can be handled by a number of third-party tools. These tools provide additional functionality that can help you manage files with long names more effectively.
- Long Path Tool: A utility specifically designed to fix issues related to long file paths.
- 7-Zip: Compressing files into a ZIP archive and then extracting them in the desired location can sometimes bypass the long path limitation.
2.6 Rename Files and Folders
The last practical solution is to shorten the names of files and folders. For example, you can abbreviate lengthy folder names or use concise file names. Renaming can often reduce the total path length to within the allowed limit.
To rename a file or folder: Right-click the file or folder > choose “Rename” > Enter a Shorter Name and press “Enter“.
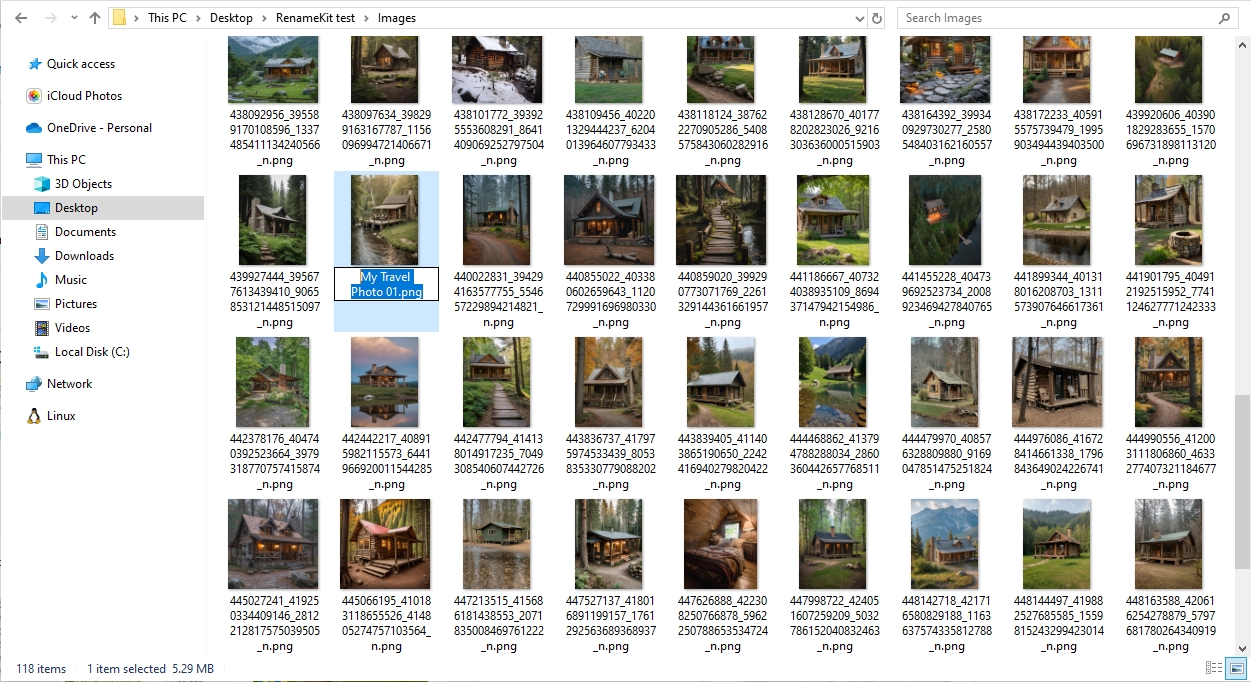
If you have many files or folders to rename, you can try RenameKit by following these steps:
Step 1: Download and install the RenameKit software on your Windows or Mac computer.
Step 2: Import file and folders into software, you can shorten filenames by configuring renaming settings: such as use the FileName Range feature to choose filenames to a specified length, the Replace Text option to remove or replace long text segments, and the Add Prefix/Suffix feature to append a short prefix or suffix for clarity.
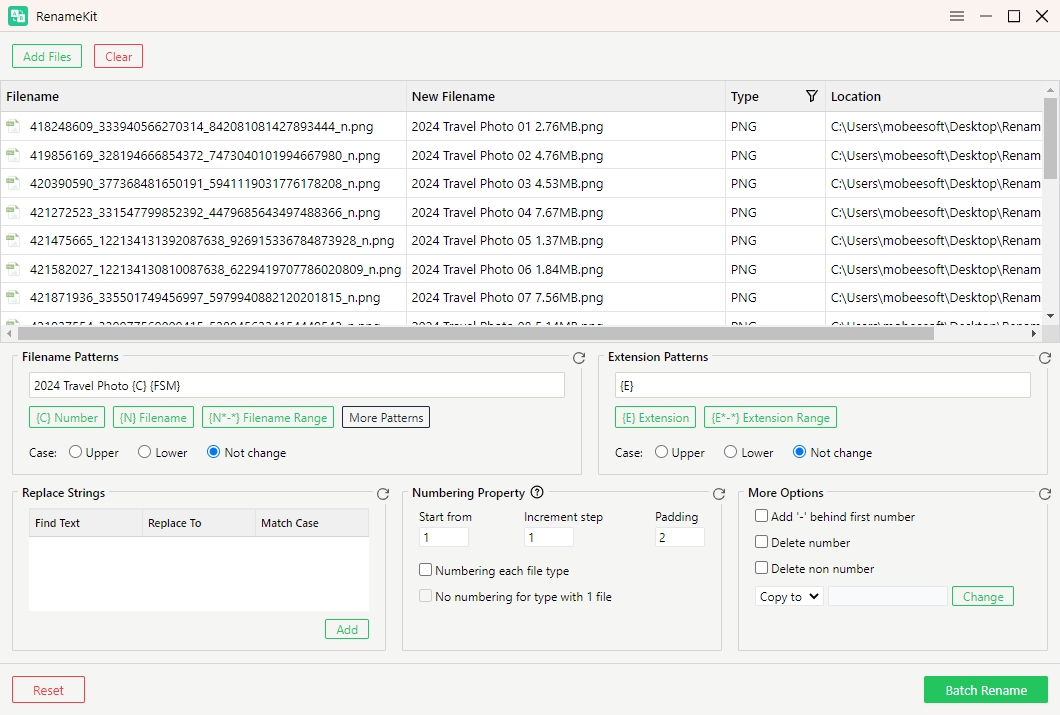
Step 3: Preview and click “Batch Rename” button to apply the shorten filenames.
Conclusion
Efficient file management is crucial, but the “filename or extension is too long” error can complicate matters, particularly with Windows’ 260-character path limit. To address this, you can enable long path support in Windows, shorten file paths, use Command Prompt or PowerShell, map network drives, or employ third-party tools.
For users seeking a more streamlined approach, especially when dealing with numerous files, using a dedicated renaming tool like RenameKit can significantly simplify the process. RenameKit allows for bulk renaming, letting you shorten filenames efficiently through features such as truncation, text replacement, and prefix/suffix addition.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage and overcome the limitations associated with long filenames and paths, ensuring a more organized and efficient file management experience.